Introduction
L'objectif de ce projet etait d'utiliser Matlab et Simulink pour modeliser, simuler et commander un robot a deux roues base sur le systeme Lego Mindstorms EV3. Le projet nous a permis d'explorer plusieurs techniques de commande, notamment la commande proportionnelle, la commande proportionnelle-integrale et la commande par retour d'etat pour stabiliser le systeme.
Introduction
The objective of this project was to use Matlab and Simulink to model, simulate, and control a two-wheeled robot based on the Lego Mindstorms EV3 system. The project allowed us to explore several control techniques, including proportional control, proportional-integral control, and state feedback control to stabilize the system.
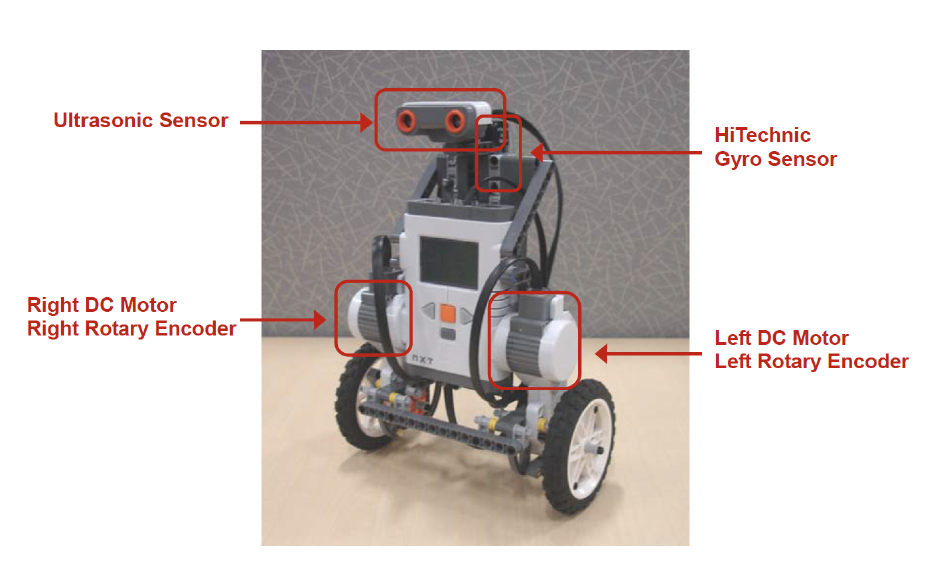
Parametres du robot
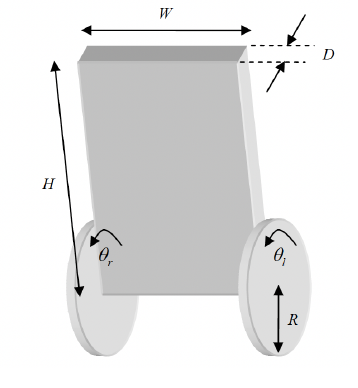
Le robot a deux roues a ete modelise a partir des parametres suivants :
- Constantes physiques : Acceleration gravitationnelle g=9.81m/s2
- Parametres Lego Mindstorms :
- Poids des roues m=0.03kg
- Rayon des roues R=0.042m
- Poids du corps M=0.67kg
- Largeur du corps W=0.165m
- Hauteur du corps H=0.152m
- Distance du centre de masse L=H/2
- Coefficients de frottement fm=0.0022 = fw=0
A partir de ces parametres, nous avons calcule les constantes utilisees dans la dynamique du systeme :
Robot Parameters
The two-wheeled robot was modeled based on the following parameters:
- Physical Constants: Gravity acceleration g=9.81m/s2
- Lego Mindstorms Parameters:
- Wheel weight m=0.03kg
- Wheel radius R=0.042m
- Body weight M=0.67kg
- Body width W=0.165m
- Body height H=0.152m
- Center of mass distance L=H/2
- Friction coefficients fm=0.0022 = fw=0
From these parameters, we calculated the constants used in the system dynamics:
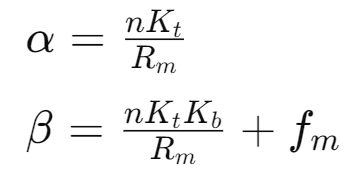
Modelisation du processus
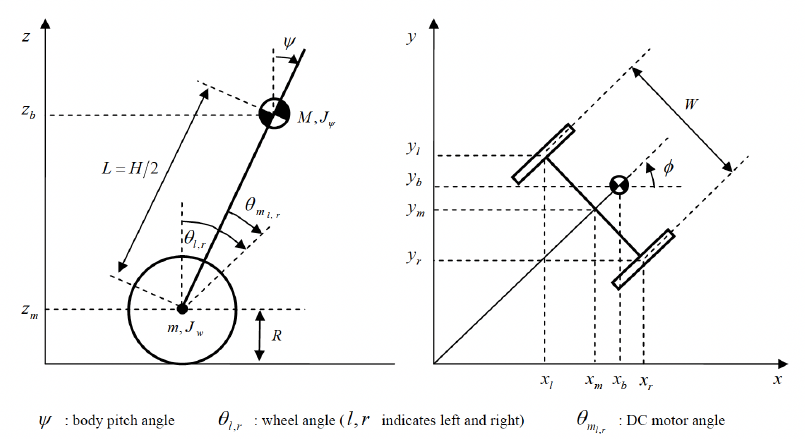
Modeles d'etat MIMO
La representation d'etat du systeme a ete derivee en modelisant le mouvement du robot a l'aide de la methode de Lagrange. Les matrices suivantes definissent le systeme :
Process Modeling
MIMO State-Space Models
The system's state-space representation was derived by modeling the robot's motion using the Lagrangian method. The following matrices define the system:
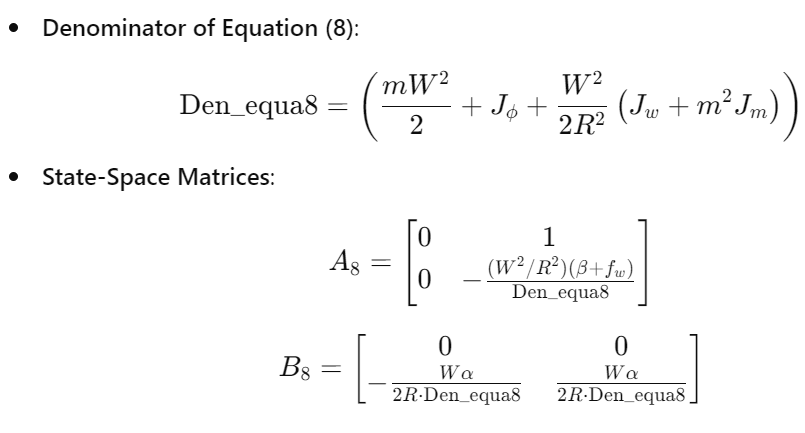
Modele d'etat SISO
Nous avons reduit le modele MIMO a un modele d'etat SISO pour le controle de l'equilibre, en simplifiant l'entree a u=(vl+vr)/2. Le systeme resultant a ete defini comme : sys = ss(A, B, C, 0)
Simulation du systeme avec Simulink
Nous avons d'abord teste la reponse en boucle ouverte du systeme a une entree echelon de 1V. Ensuite, nous avons teste la reponse du systeme a une entree impulsionnelle. Dans les deux cas, le systeme etait instable, car le signal ne se stabilisait pas et continuait d'augmenter sans limite.
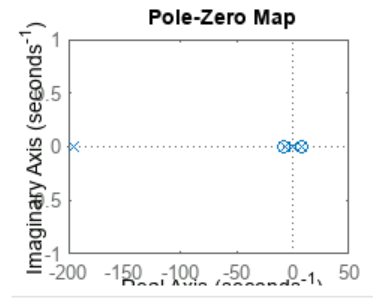
Analyse en boucle ouverte
Nous avons analyse le systeme pour l'observabilite et la commandabilite. Les rangs des deux matrices etaient egaux au rang de la matrice A, confirmant que le systeme est observable et commandable. Le systeme s'est avere instable, comme le montre la carte poles-zeros et l'analyse de l'amortissement.
SISO State-Space Model
We reduced the MIMO model to a SISO state-space model for balance control, simplifying the input to u=(vl+vr)/2. The resulting system was defined as: sys = ss(A, B, C, 0)
Simulation of the System with Simulink
We first tested the open-loop response of the system to a step input of 1V. Next, we tested the system's response to an impulse input. In both cases, the system was unstable, as the signal did not stabilize and continued increasing without bound.
Open-Loop Analysis
We analyzed the system for observability and controllability. Both matrices' ranks were equal to the rank of matrix A, confirming that the system is observable and controllable. The system was found to be unstable, as shown by the pole-zero map and damping analysis.
Conception du systeme de commande
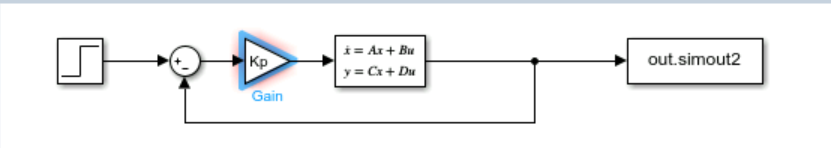
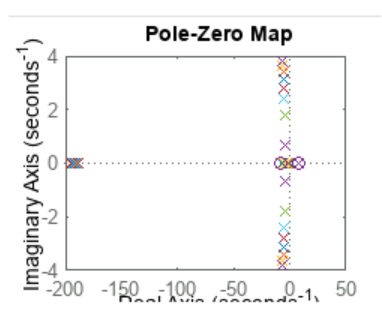
Commande proportionnelle
Nous avons implemente un correcteur proportionnel pour stabiliser le systeme. Malgre la variation du gain Kp, le systeme est reste instable :
Control System Design
Proportional Control
We implemented a proportional controller to stabilize the system. Despite varying the gain Kp, the system remained unstable:
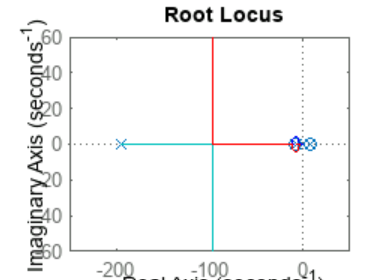
Commande proportionnelle-integrale
Ensuite, nous avons implemente un correcteur proportionnel-integral (PI). Cependant, le systeme est reste instable pour toute combinaison de Kp et Ki, car l'analyse du tableau de Routh a montre qu'il y avait toujours des termes positifs dans la premiere colonne :
Proportional-Integral Control
Next, we implemented a proportional-integral (PI) controller. However, the system remained unstable for any combination of Kp and Ki, as the Routh table analysis showed that there were always positive terms in the first column:
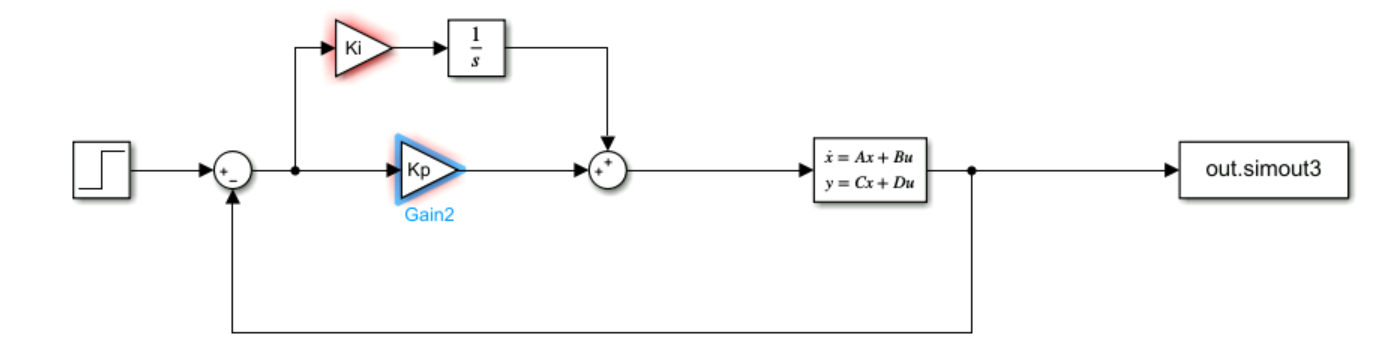
Commande par retour d'etat
Enfin, nous avons implemente un correcteur par retour d'etat, qui a reussi a stabiliser le systeme. Cependant, le signal de commande presentait une erreur significative, que nous avons corrigee en ajoutant un pre-gain lc.
State Feedback Control
Finally, we implemented a state feedback controller, which successfully stabilized the system. However, the control signal exhibited significant error, which we corrected by adding a pre-gain lc.
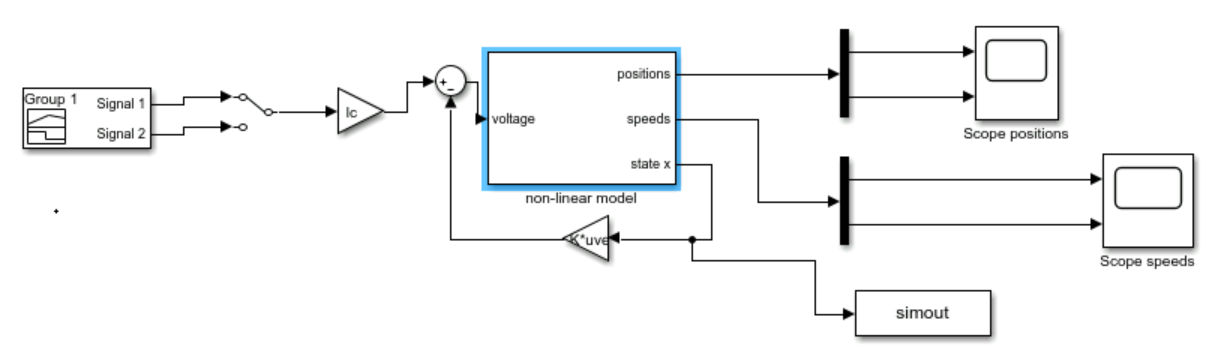
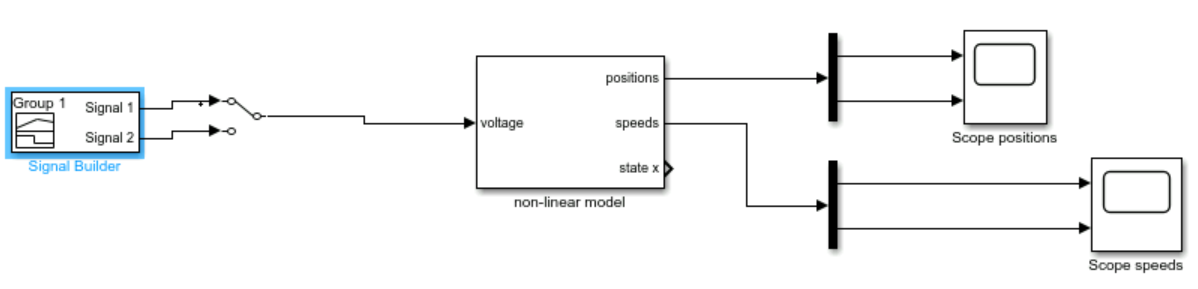
Simulations non-lineaires
En utilisant le fichier Simulink NXTwaySim fourni, nous avons realise des simulations non-lineaires pour valider les lois de commande. Sans retour d'etat, le systeme etait instable, mais avec le retour d'etat, le robot maintenait son equilibre :
Nonlinear Simulations
Using the provided NXTwaySim Simulink file, we performed nonlinear simulations to validate the control laws. Without feedback, the system was unstable, but with state feedback, the robot maintained balance:
Conclusion
Ce projet nous a permis d'explorer et d'appliquer differentes techniques de commande a un systeme complexe du monde reel en utilisant Matlab et Simulink. Alors que les correcteurs proportionnels et PI n'ont pas fourni la stabilite necessaire, le correcteur par retour d'etat s'est avere etre une solution efficace. Le projet a mis en evidence l'importance du retour d'etat dans la stabilisation de systemes ou les strategies de commande plus simples echouent.
Le projet a egalement fourni une experience precieuse dans la modelisation et la simulation de systemes de commande et a approfondi notre comprehension des concepts theoriques abordes en cours.
Conclusion
This project allowed us to explore and apply various control techniques to a complex, real-world system using Matlab and Simulink. While proportional and PI controllers did not provide the necessary stability, the state feedback controller proved to be an effective solution. The project highlighted the importance of state feedback in stabilizing systems where simpler control strategies fail.
The project also provided valuable experience in modeling and simulating control systems and deepened our understanding of the theoretical concepts covered in class.